In recent years, sustainability has taken center stage, capturing the attention of all stakeholders in the agricultural supply chain. From food and beverage companies to agricultural supply chain companies and even farmers themselves, everyone is feeling the impact. With consumers and investors increasingly demanding environmental, social, and governance (ESG) accountability, the pressure to meet ESG compliance standards has never been higher.
Now, you may wonder – what exactly do these ESG compliance standards entail? How do they specifically relate to agri-food companies?
These questions are crucial in understanding the impact of regulations like the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS), which are spearheading the sustainability shift in the EU.
Table of Contents
Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and Agri-Food Value Chain
As global efforts continue to address climate change concerns and the actions needed to combat its effects, regulators are now increasingly looking especially at the food and beverage industry’s impact, owing to its focus on value chain accountability and a huge share of Scope 3 GHG emissions that include emissions of farmers in their supply chain.
Namely, the food value chain is notoriously fragmented and often accounts for a huge share of F&B’s environmental impact. As agriculture is one of the largest sources of GHG emissions, for many food and beverage companies, Scope 3 will likely constitute an average of 89% of total emissions and companies will have to make significant investments in agricultural supply chains in order to reduce and control them. In light of this, it becomes crucial for F&B companies to focus on environmental data sourcing and reporting. By obtaining accurate and comprehensive data on their environmental impact, they can identify areas for improvement, implement targeted strategies, and track their progress over time.
Let’s briefly dive into the main terminology.
- the Corporate Sustainability Directive (CSRD) is a new sustainability reporting framework that mandates companies to provide standardized, comprehensive data on their sustainability performance and climate risks. It ensures investors and stakeholders have comparable information to evaluate companies’ impact and risks across their value chain. Companies are required to report this data digitally and incorporate it into their annual reports.
- the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) is a set of reporting requirements created in line with the EU taxonomy and multiple other voluntary reporting frameworks, in a stated effort to standardize and harmonize reporting.
The CSRD extends the scope and reporting requirements of the Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD) and aims to ensure businesses report comparable and reliable sustainability information in order to orient investors and other stakeholders to favor more sustainable companies. Among other things, the CSRD covers issues of:
- climate change mitigation efforts and KPIs;
- social responsibility across the value chain;
- governance issues such as anti-corruption and diversity.
While all the ESRS are relevant to any company’s reporting, companies whose value chains include agricultural production, like food and beverage companies, need to pay special attention to 7 key standards:
How Agri-Food Companies can Leverage Digital Agriculture Solutions to Meet CSRD Requirements?
Gaining insights into the practices and inputs used throughout the production value chain is crucial for fostering sustainable practices and achieving ESG compliance for agri-food companies. Collecting data from various stakeholders involved allows companies to understand the overall production process, identify potential risks, and take necessary steps to mitigate them. This data is invaluable in ensuring that companies have accurate and reliable information for their reporting systems.
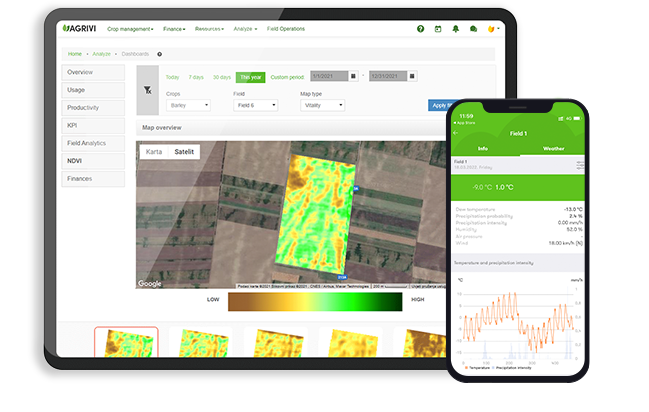
This is where AGRIVI farm management platform comes as enormous help as a simple way to secure the farming data needed for ESG reporting by providing valuable insights into the sustainability of the supply chain specifically related to own crop production or contracted crop production. Farm management platform provides real-time agronomic and economic insights throughout the entire food production process. Through one centralized digital platform, companies can manage the entire supply chain with features like precise fertilization recommendations, real-time weather monitoring, use of insecticides and pesticides, water consumption and usage tracking, soil analysis, land use change, and sustainable contracting.
Thus, by implementing AGRIVI 360 Agriculture Supply Chain platform, companies can get a comprehensive and timely overview of their farm’s activities and the precise tracking of resource usage, water usage, energy use, and other important ESG metrics for environmental segments.
With features that enable detailed record-keeping and reporting, AGRIVI enhances transparency in line with CSRD requirements, giving stakeholders clear insights into a farm’s operations.
The precision and granularity of data provided by farm management software are essential for accurate, comprehensive environmental reporting. Gathering various data like machinery and fuel usage, mineral fertilizers usage, pesticides and crop protection usage, and irrigation and water usage through AGRIVI farm management software helps companies to measure and report the current state to demonstrate compliance with regulations and standards, but also to identify areas for improvement and track the effectiveness of sustainability initiatives over time.
As the focus on the company’s impact on sustainability intensifies, there will be a growing demand for precise data that address ESG standards. For those in the food and beverage space, getting ahead of these impending regulations offers an opportunity to not only emerge as leaders but also avoid costly risks down the line.