From the very beginning, the most important necessity to sustain human life has been food. After only being able to eat wild crops and animals initially, humans then began to domesticate crops. Early farmers produced crops that had more desirable traits than wild ones. They used them as a seed source for subsequent generations of food. Thus began the era of farming.
Many crops in present-day farming are the result of the domestication that took place in ancient times. Farmers grow them to use as food, feed for domestic animals, fiber, clothing, shelter, and energy production. Although crops are classified based on climate, season, land use, type of product, and economic importance, the most important classification is based on farming types and growing cycles of arable crops, vegetables, and permanent crops.
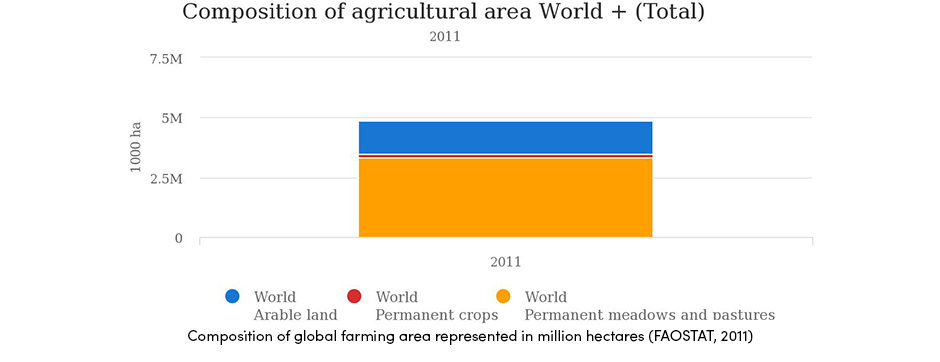
According to statistical data, 11 percent (1.5 billion ha) of the globe’s land surface (13.4 billion ha) is used for crop production of arable crops, vegetables, and permanent crops. This area represents slightly over one third (36 %) of the land estimated to be suitable for crop production.
In the global farming area that is suitable for crop production, arable land occupies 28.6 %, permanent crops 3.2 % and permanent meadows 68.5 %Statistically, vegetable production is included with arable crops and it covers only 1.1 % of the world’s total agricultural area.
Crop production starts with proper soil preparation and planting of transplants or sowing of seeds. The planting method, time spent, and soil preparation practices that a farmer will use depends primarily on the crop type, whether it is a fruit, vegetable or arable crop.
Aspects to Consider Prior to Planting Fruit Trees
Prior to fruit tree planting, the field needs to be leveled, planting rows determined, and planting holes well-prepared. Every fruit crop requires certain row and plant spacing in order to provide optimum yield performance. Spacing varies depending on the crop variety, crop production system, and planned yield. Usually, fruit transplants that are 1-3 years old are planted.
Aspects to Consider Prior to Planting Vegetables and Arable Crops
Unlike fruit trees, vegetables and arable crops are annual crops which require a seasonal change of planting surface. This farm practice is called crop rotation and has many beneficial effects on crop properties and total yield.
Both arable crops and vegetables can be planted directly using seeds and transplants. Transplants are young plants (few weeks old) that are produced first in the greenhouse or in the field in order to promote faster growth, higher resistance to abiotic stress, and various pests. Producing quality fruits and a high yield is also a goal of this practice.
Producing crops from transplants requires special preparation, both of planting rows and holes. Another thing to consider is spacing. This will determine both crop performance and yield.
Factors Which Determine Efficacy of Crop Production
In any crop production management system, many factors must be considered prior to planting in the field. Together, these factors will also determine which planting method a farmer should use; direct sowing or planting of transplants. Essential factors which will determine efficacy of crop production are as follows:
- Type of a crop – Carrot, potato, and corn are usually direct seeded, while pepper, tomato, and cassava are grown from transplants
- Growing climate
- Weather conditions at the time of planting
- Duration of the growing season
- Farmer’s financial health
- Farmer’s knowledge about farm practices
Proper planting, along with soil preparation makes up half of what is needed for successful farming. The other half is ensuring proper crop maintenance during the growing season as well as timely harvesting. The ability to effortlessly combine all of these farming practices is one characteristic of a successful farmer.
Image sources: FAO