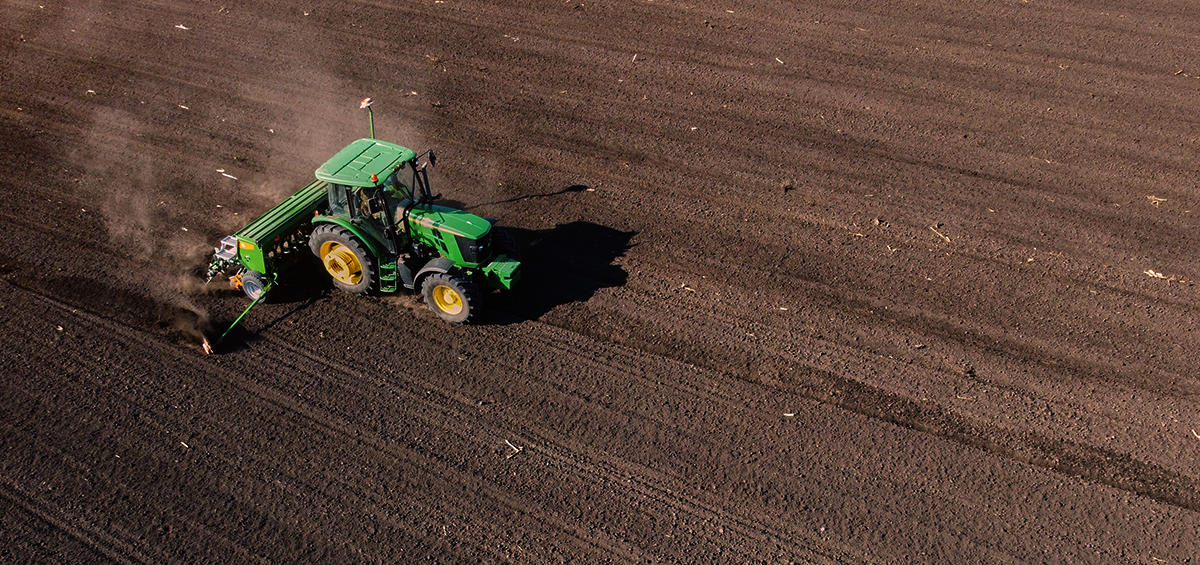
The soil preparation is the first step to ensure that the field is ready for growing a crop. A well-prepared field controls weeds, recycles plant nutrients, and provides a soft soil mass for transplanting and a suitable soil surface for direct seeding.
Land preparation involves plowing to “till” or dig-up, mix, and overturn the soil, harrowing to break the soil clods into smaller mass and incorporate plant residue, and leveling the field.
Initial land preparation for autumn sowing begins after harvesting of previous crop and continues until sowing or planting of next crop, which is important for effective weed control and for the soil enrichment with organic compounds.
Soil tillage is generally divided into basic and additional tillage. If the previous crop is cereal, basic tillage begins with very shallow plowing, otherwise it begins with shallow plowing at a depth of 20 cm. The goal of basic tillage is to bring the soil into the state of quality structure and to create a seedbed in the surface layer to a depth of sowing. The goal is to create ideal conditions for the germination of small and sensitive plants.
Pre-sowing soil preparation creates a seedbed for optimal conditions for germination of seeds and easy sprouting of young plants. This is followed by tillage for making of tiny crumb soil structure, wherein the fine soil aggregates are left on the surface, to avoid creating of crust, and around the seed is left sufficient amount of loose soil and capillary movement of water is established.
The finer seed is, the higher are requirements for machinery for soil preparation. The impact of machines for creating a seedbed on the final yield is very high. Top yields are achieved in conditions without stress, and quality germination and early seedling growth resulting in the creation of a stronger plant resistance to later disruptions caused by weather conditions.
Like tillage, fertilization is also divided into basic and additional. Immediately after plowing, NPK fertilizers are entered into the soil, whether of plant, animal or mineral origin, depending on product type, with higher amounts of phosphorus and potassium. The amount of fertilizer must be sufficient to compensate the number of fertilizers that the previous crop took out from the soil and to meet the needs of a crop that will be grown. To determine the exact amount of fertilizers, it’s necessary to make a chemical soil analysis, to see the exact nutritional status of the soil. Just before sowing or planting of the crop, NPK fertilizers with nutrients ratio 1: 1: 1 are entered, which can be combined with pure nitrogen fertilizers, especially if a long dry period is followed.
The whole process of preparing the soil for sowing or planting takes only 3-4 weeks, depending on the farmer’s capabilities and weather conditions, and this is one of the most important parts of farm production. To avoid mistakes from the start, it’s very essential to have knowledge of the farm processes, which provides you AGRIVI farm system. For over 100 different crops, for all types of production, the system guides you how to prepare the soil for sowing or planting on the best way, and shows you all activities you have to do in the field, even though the soil has never been cultivated. Beside all this, the system allows you to manage the entire farm production, from tracking of tasks, used materials, inventory, finances and reports to the analysis of productivity and profitability of the entire farm production.
Learn how to prepare the soil well with AGRIVI system, because good seedbed preparation is the foundation for achieving a maximum crop productivity.