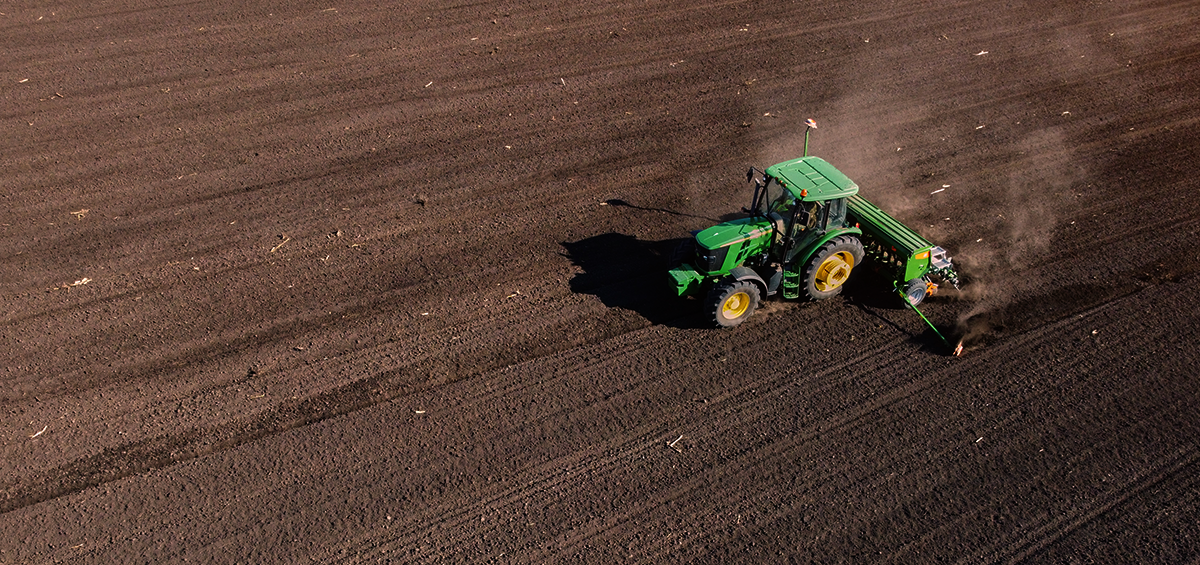
The sowing of winter crops is reaching its deadline. Therefore, it’s time for farmers to finish field preparations and start to sow winter cereals such as wheat, barley, oat, rye, triticale or fodder crops like legumes and kale. Farmers from all over the world work hard throughout the year. However, in moderate climates such as Europe and the USA, farming is seasonal. These farmers have separated sowing periods into spring and fall sowing. After the summer harvest is finished, farmers immediately start with farm practices for the sowing of winter crops. Farmers often have concerns about the right time for the sowing of winter crops. The time for sowing primarily depends on the crop variety, its requirements, local climatic conditions and soil type. Therefore, it’s a common practice among farmers to choose the earliest recommended sowing time in order to maximize the full crop potential. By following good farm practices and proper sowing management, a farmer can increase yields and reach the highest overall farm profit.
Soil Preparation
High quality and healthy soil is the basis of successful farm management. By using the best soil preparation practices, farmers can ensure that they have well-prepared soil that manages weeds, recycles plant nutrients, provides a soft mass for sowing and a suitable surface for seeds. The soil preparation includes:
- Liming, which is a practice to improve soil quality in case the soil analysis shows a lack of calcium ions, i.e. the soil is too acidic
- Very shallow plowing, a practice used if the previous crop was cereal. The purpose of this practice is to break the system of capillaries in the surface layer, to prevent the growth of weeds and to introduce crop residues into the soil which enhance the activity of microorganisms
- Shallow plowing, should be applied when the previous crop wasn’t cereal. The plowing to depths of 10-20 cm encourages the destruction of sprouted weeds
- Final surface soil tillage (including disking) cuts, crushes and mixes the soil
- Harrowing brakes crust to an average depth of 6 cm, aggregates soil structure, aligns the surface and destroys weeds.
Final surface tillage: disking and harrowing
Fertilization
Fertilization with manure is recommended for the improvement of microbiological soil activity. In conventional production, farmers should apply manure every 3-5 years to enhance soil properties and humus levels. The best practice is to first apply manure and then, during the soil tillage, add mineral fertilizers. One part of mineral fertilizers is added before sowing and the other part after crop emergence, during crop maintenance.
Sowing
Sowing is the final phase before the new crop cycle starts. The final preparation practice that creates a straight, grained, structural and moist sowing layer is pre-sowing plowing. It can be combined with fertilization. After the soil preparation is finished, a farmer has to determine canopy density. This depends on the soil type, crop and the purpose of sowing a certain crop. Once all farm preparations are completed, sowing can begin.
Fall sowing of winter crops
The complete preparation and sowing process takes from 3-4 weeks, depending on the farmer’s management capabilities and weather conditions. It’s important to avoid mistakes at the start because sowing is the most important part of farm production. To ensure proper management practices for sowing, farmers can rely on AGRIVI farm management software. With Agrivi, they can easily plan the whole crop season for any crop and manage their farm activities. The software provides the knowledge base for soil preparation in the form of tasks for more than 100 crops for all production types. With AGRIVI, farmers can also keep records of soil analysis and crop rotation.
Manage your new crop season successfully, by using AGRIVI!
Image sources: Stonny Hill || Tupanjac || E Zadar