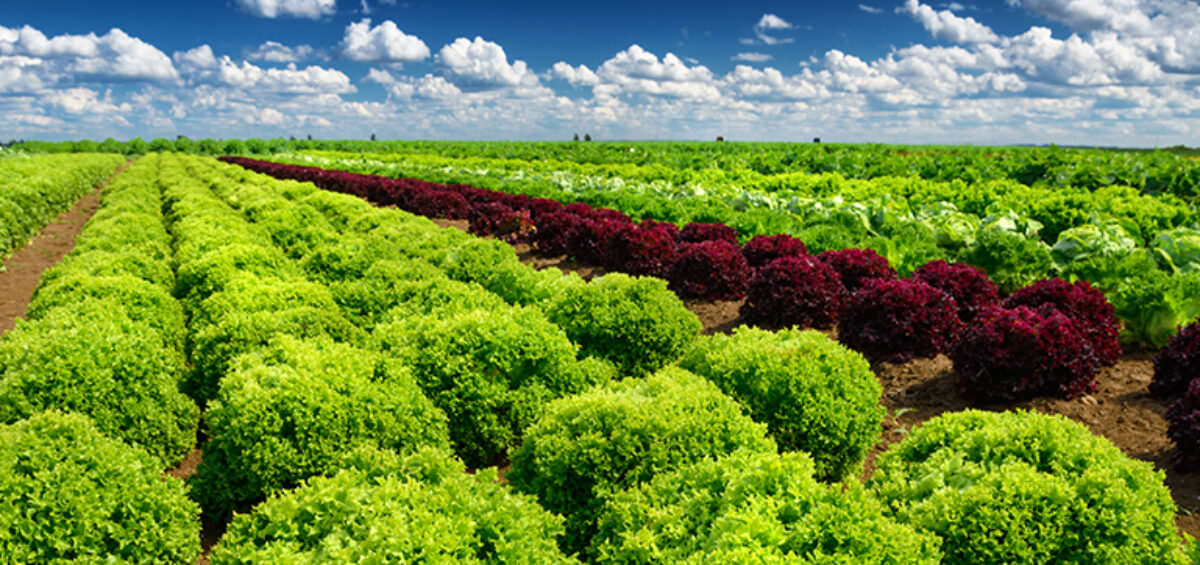
Vegetable farming is a type of crop production intended primarily for human consumption of the crop’s edible parts such as the shoot, leaves, fruits, and roots. According to the consume part of the crop, vegetables are divided into the following groups:
- Leaf vegetables (lettuce, cabbage, spinach)
- Fruit vegetables (pepper, cucumber, tomato)
- Root vegetables (carrot, radish, sweet potato)
- Bulb vegetables (garlic, onion, fennel)
- Flower vegetables (artichoke, cauliflower, broccoli)
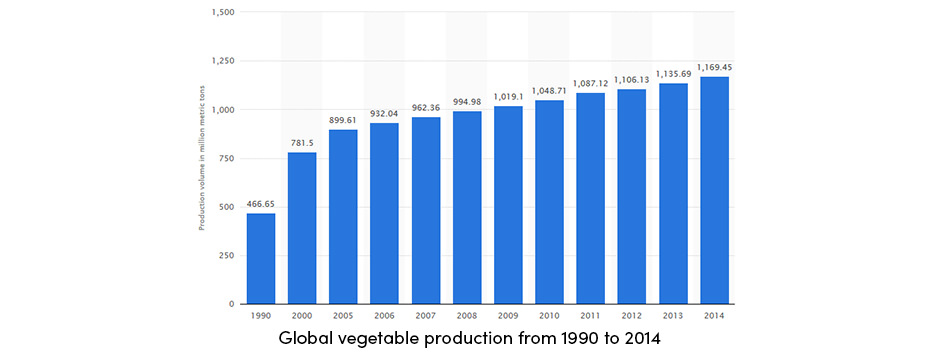
Global vegetable crop production has consistently increased in recent years. The growth of vegetable production is shown in the table below.
Despite the fact that vegetable farming is a labor-intensive practice, it’s very popular among farmers as a high-income branch of farming. The secret to vegetable farming profitability lies in its high market price of crops, as well as in high demands for vegetables year-round.
Moreover, growing of vegetables is a preferable farm practice in developing and food-insecure countries. Since vegetables are rich in vitamins, minerals, and fibers, they play an important role in diet improvement.
Differences in the Sowing and Planting of Vegetables
Growing of vegetables starts with sowing or planting. Vegetable sowing means putting a seed directly into the prepared soil. On the other hand, vegetable planting includes the practice of putting already grown seedlings into the soil. Seedlings can be grown in the field or in greenhouses.
There are two types of seedlings:
- Bare root seedlings are grown in the field from the seed. As the name implies, their roots are separated from the soil when they are moved to the planting site.
- Root ball seedlings are grown in pots or blocks and moved to the planting site with the soil attached to the roots.
Sowing is a recommended practice for vegetables with delicate roots and taproots, such as carrots, turnips, and radishes. Growing of vegetables from seedlings is more appropriate in cases such as slow-growing perennials, crops with fine and expensive seed, and warm-season crops. Planting is recommended for annual vegetable crops when the soil is too cold or moist for direct sowing. For example, onion and asparagus are vegetables that are usually planted.
Factors that Determine Successful Vegetable Production from the Early Beginnings
Whether the growing of vegetables is intended for fresh consumption, processing, or seed production, it can be a profitable business. However, there are a few factors that may influence the profitability of vegetable production from its early beginnings:
- Seed quality; sowing of quality, clean, labeled, graded to size, viable, and healthy seed can make all the difference between success or failure in vegetable farming
- Optimal time of sowing/planting; depends on climate and environmental conditions of the specific area, as well as requirements of each crop
- Method of planting; the secret to successful vegetable farming lies in the managing of optimal crop requirements, by combining production of transplants in the greenhouses with planting in the field
Finally, considering effective farm management is the first step in creating profitable vegetable production. In essence, farming of these colorful crops can be a profitable business.
Text sources: Federal University of Agriculture, Abeokuta
Image sources: Statista Inc.
Digitalization in Agriculture Leading to More Productive and Profitable Vegetable Production
Digitalization is a key to more efficient, productive, and profitable agriculture. It enables farmers to make data-driven decisions based on real-time insights, and thus improve their farm operations, perform regenerative and more sustainable farming practices, and reach more productive and profitable crop production.
Farm management software systems (FMS) such as AGRIVI are particularly promising because they can equip farmers with data and information needed to evaluate and manage how they utilize large value pools, including inputs such as fertilizers, seeds, and pesticides, machinery, labor or finance.
Farm Management Software provides a centralized platform for data collection, analysis, and management. AGRIVI Farm Enterprise implemented in an agricultural operation leads to reduced expenses, increased yields, better yield quality, higher profitability and lower operational risk.
Learn more:
AGRIVI customers optimized their farm operations and increased profitability up to 15%. You can too!
Read the customer story and find our how one of the biggest vegetable producers on Baltic improved their productivity and profitability with AGRIVI: